The city of Lvov (L’viv) in southeastern Poland was occupied by the Soviet Union in 1939, under the terms of the German-Soviet Pact. There were over 200,000 Jews in Lvov in September 1939; nearly 100,000 were Jewish refugees from German-occupied Poland.
The Germans subsequently occupied Lvov after the invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941.
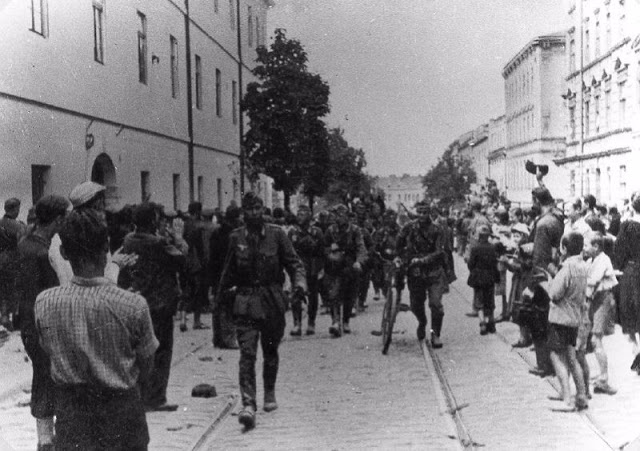
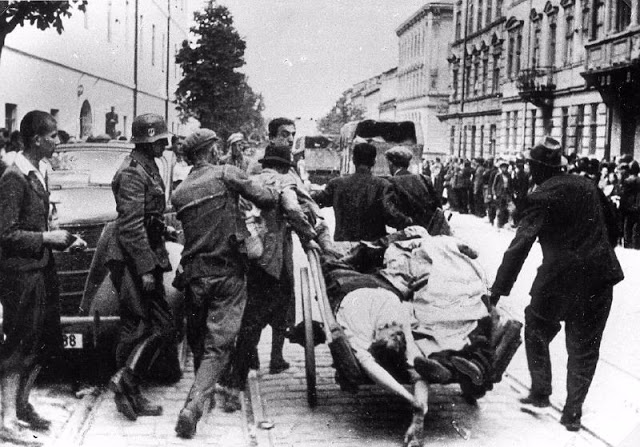
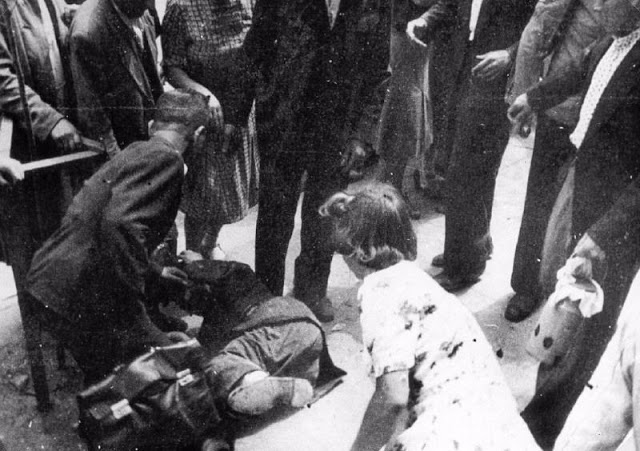
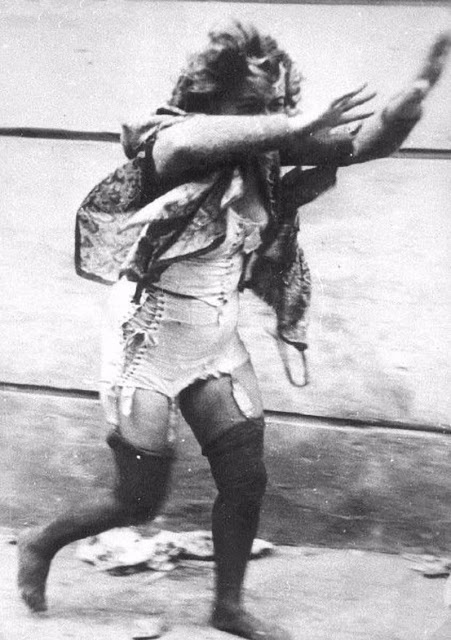
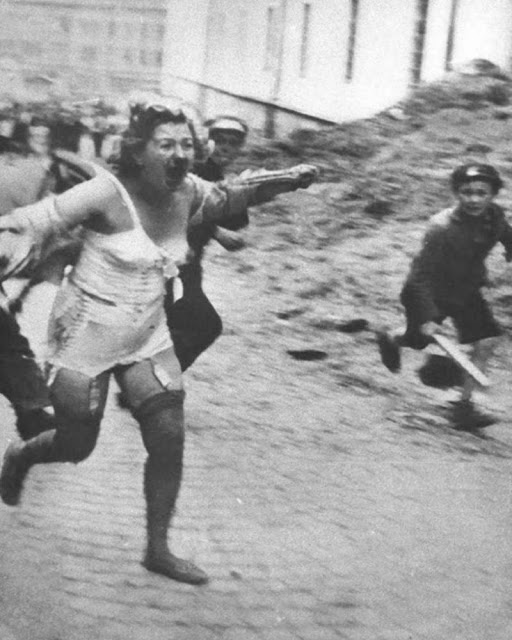
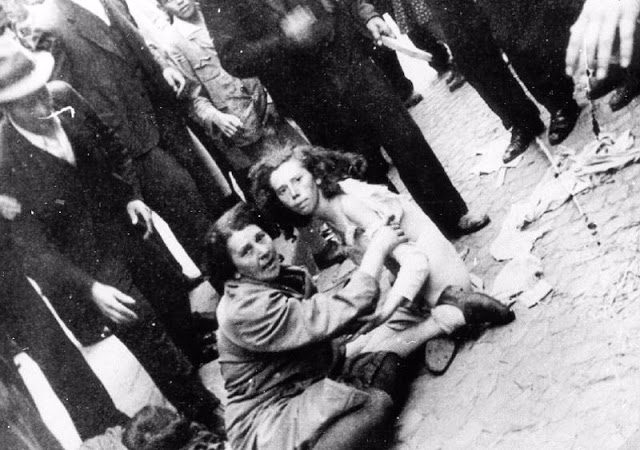
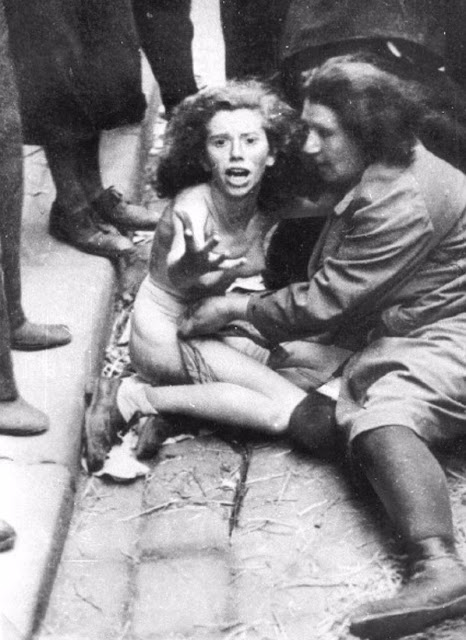
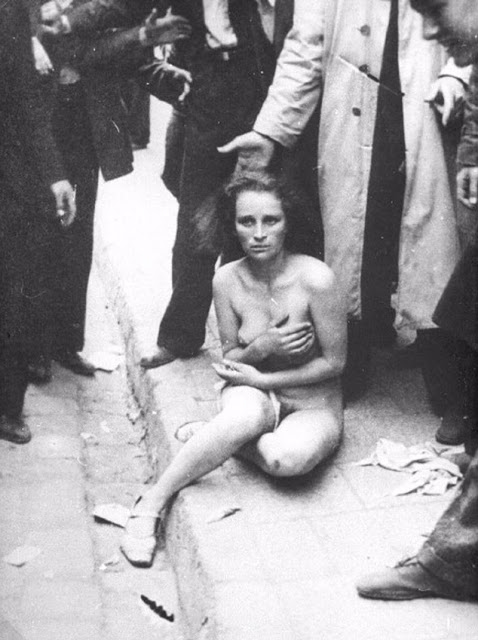
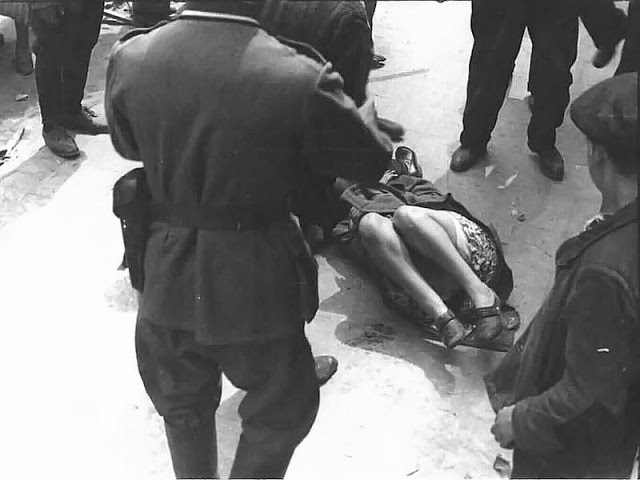
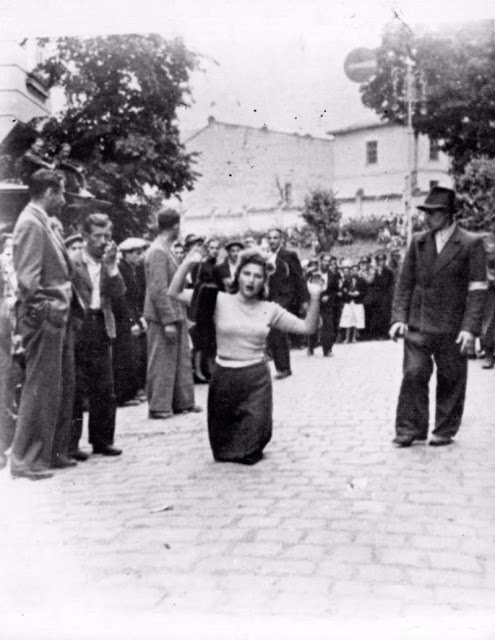
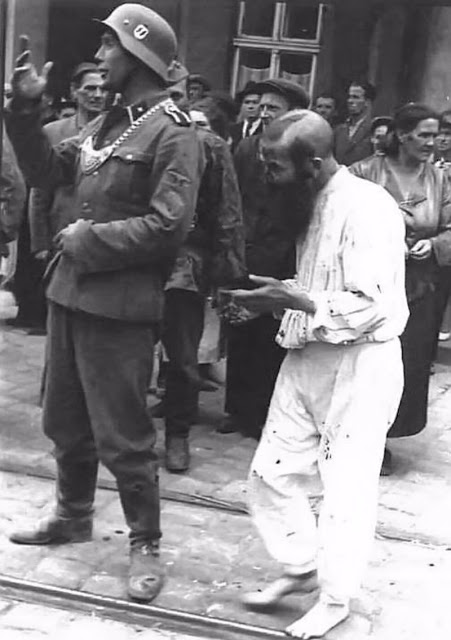
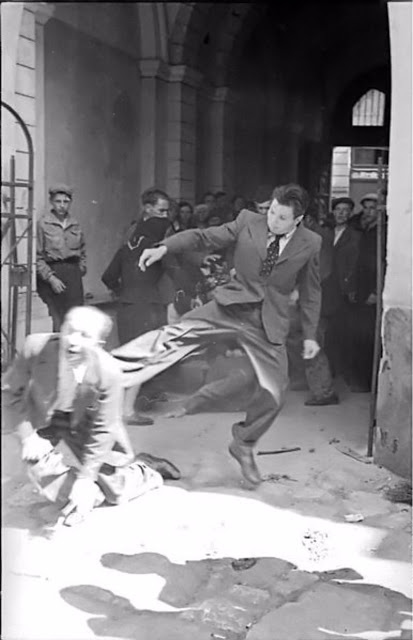
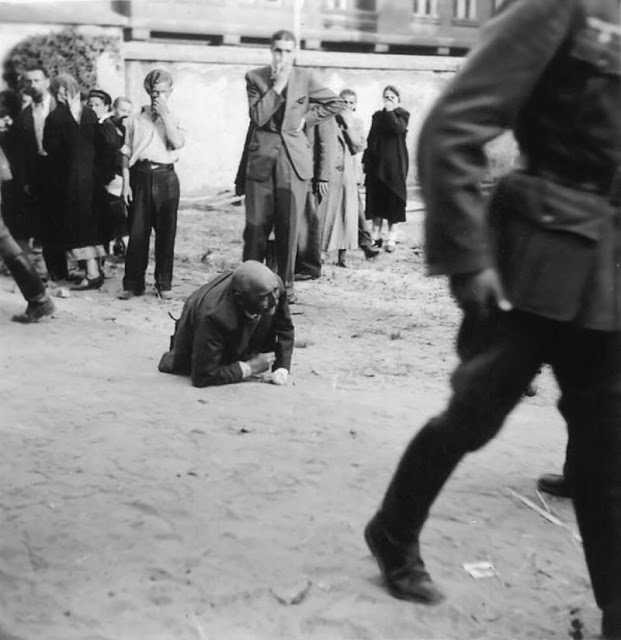
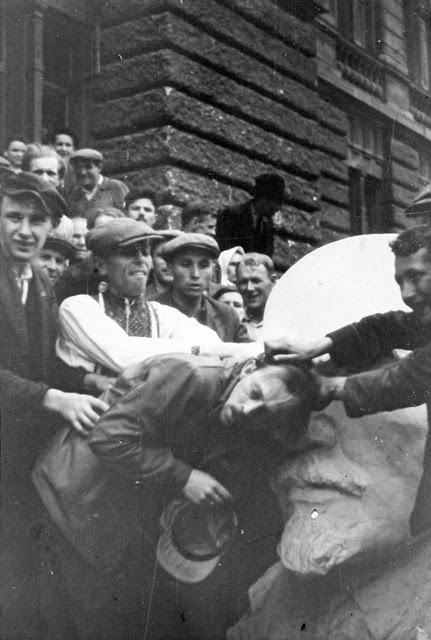
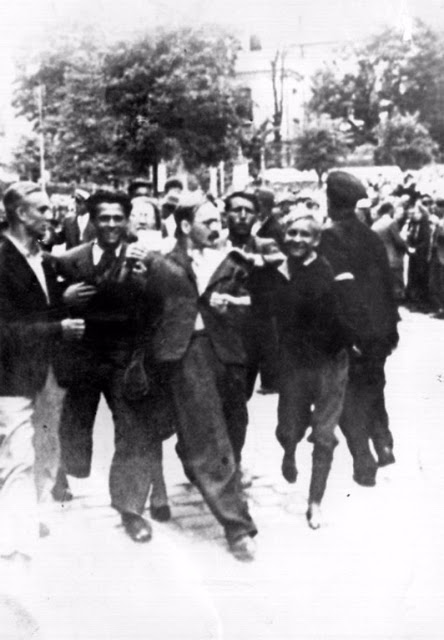
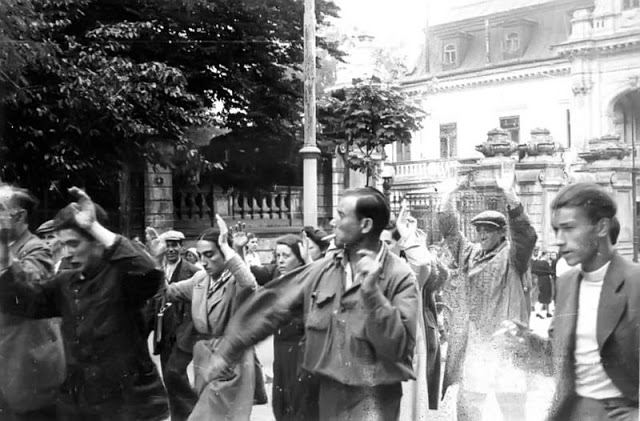
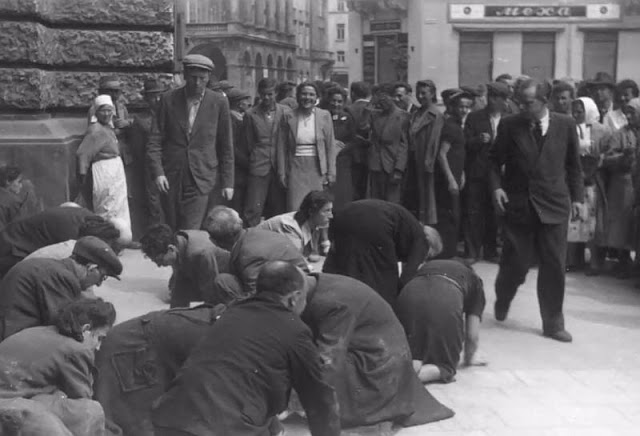
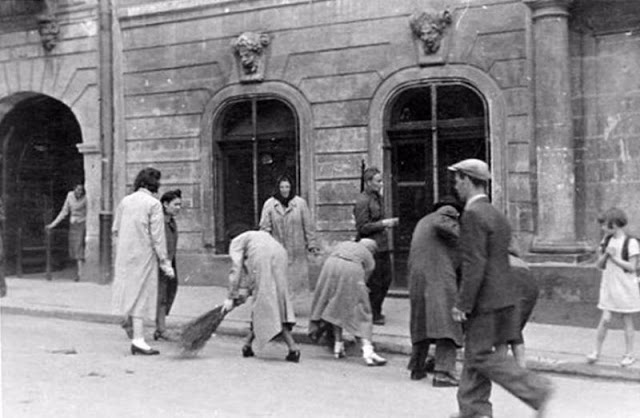
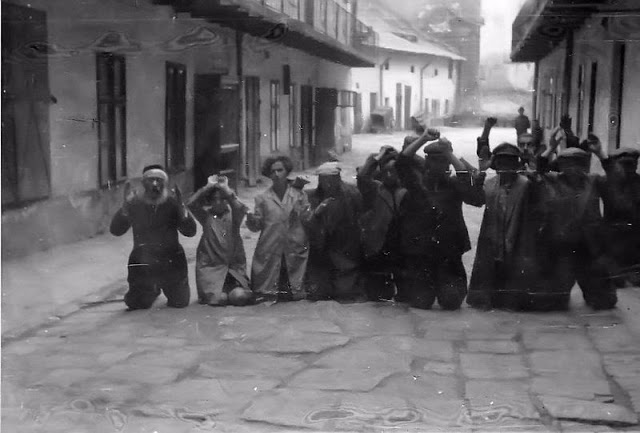
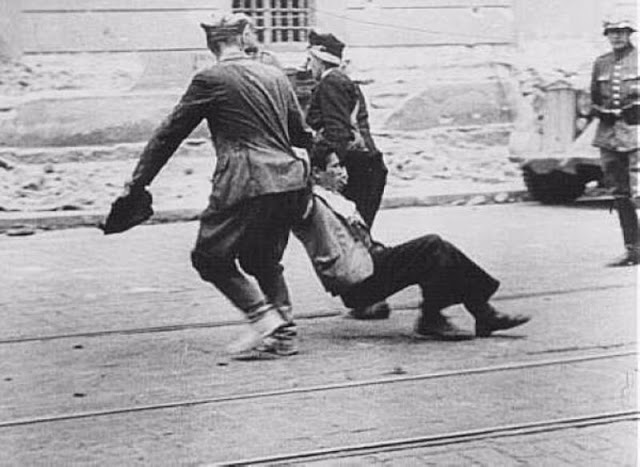
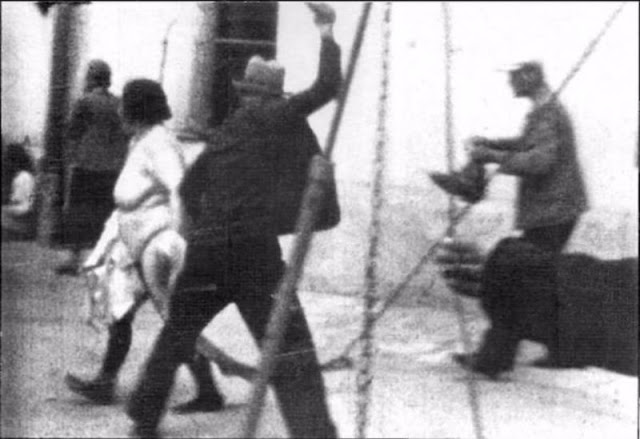
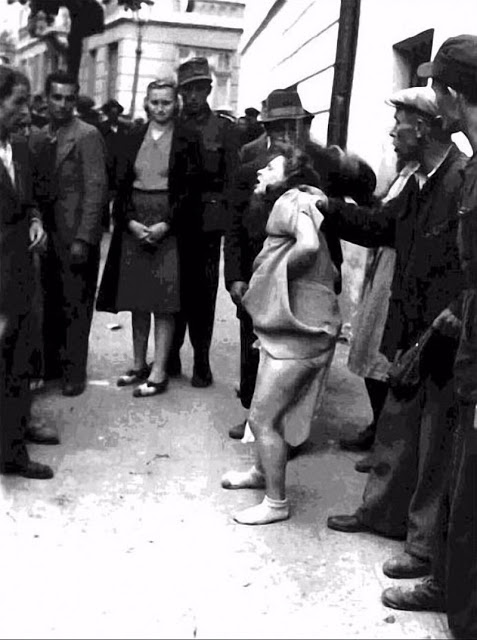
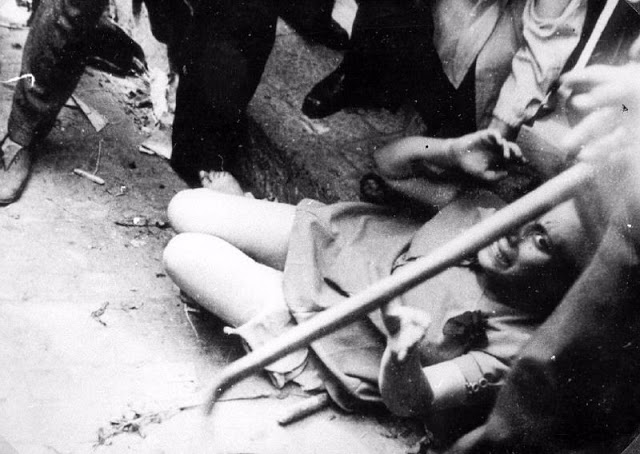
Encouraged by German forces to begin violent actions against the Jewish population in Lvov, Ukrainian nationalists massacred about 4,000 Jews in early July 1941.
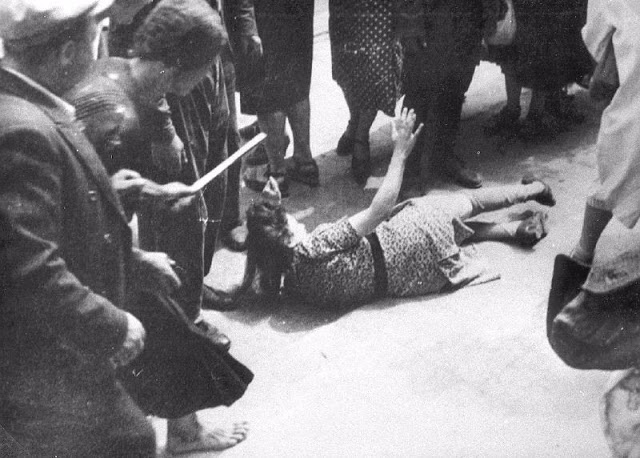
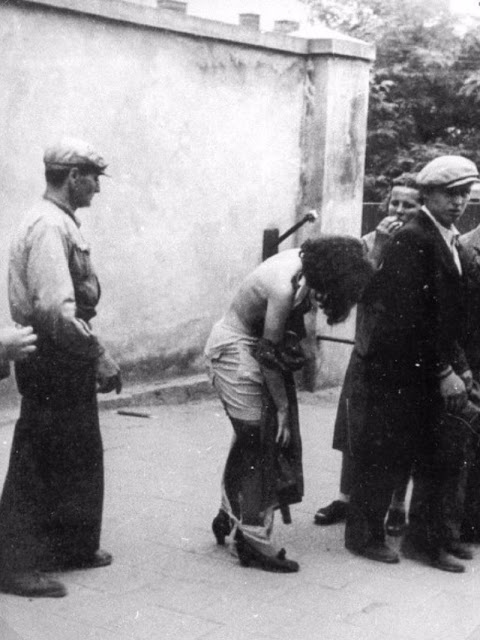
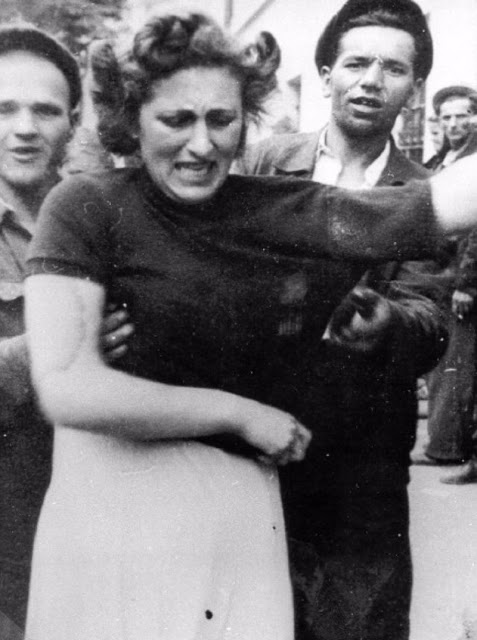
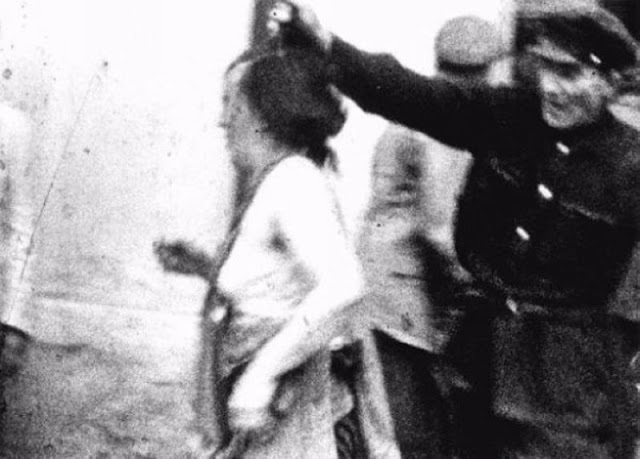
Another pogrom, known as the Petliura Days, was organized in late July. This pogrom was named for Simon Petliura, who had organized anti-Jewish pogroms in the Ukraine after World War I.
For three days, Ukrainian militants went on a rampage through the Jewish districts of Lvov. They took groups of Jews to the Jewish cemetery and to Lunecki prison and shot them. More than 2,000 Jews were murdered and thousands more were injured.

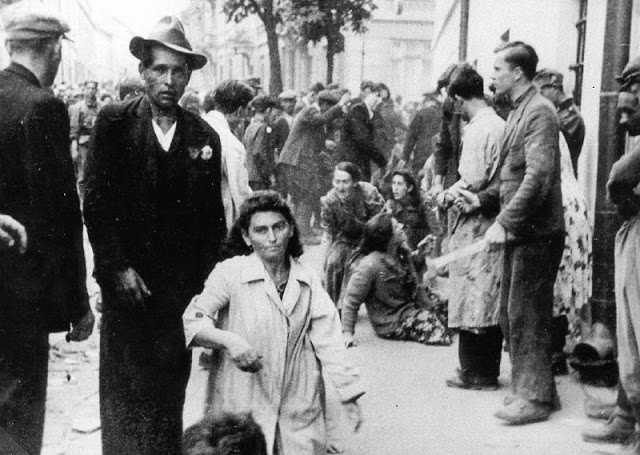
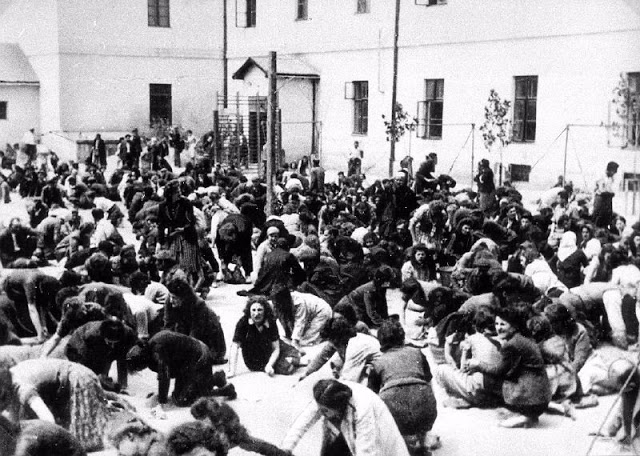
In early November 1941, the Germans established a ghetto in the north of Lvov. German police shot thousands of elderly and sick Jews as they crossed the bridge on Peltewna Street on their way to the ghetto.
In March 1942, the Germans began deporting Jews from the ghetto to the Belzec extermination camp.
By August 1942, more than 65,000 Jews had been deported from the Lvov ghetto and murdered. Thousands of Jews were sent for forced labor to the nearby Janowska camp.
In early June 1943, the Germans destroyed the ghetto, killing thousands of Jews in the process. The remaining ghetto residents were sent to the Janowska forced-labor camp or deported to Belzec.